Heatwaves in the Philippines
Impact on Students’ Well-being and Academic Performance

Introduction
Right now, the Philippines is facing harsh, drawn-out heatwaves made worse by climate change. The scorching heat and oppressive humidity are making life tough for everyone. It’s not just about feeling uncomfortable; it’s affecting farming, people’s health, and city life. And those hit the hardest are the ones already vulnerable, like the elderly and kids. With extreme weather becoming more common, it’s crucial to grasp and tackle the effects of these heatwaves to protect the nation’s strength and welfare.
Overview
Heatwaves are extended periods of unusually high temperatures, typically lasting for several days or even weeks, surpassing the seasonal average. In the Philippines, where tropical climates are prevalent, heatwaves are intensified by factors like high humidity levels and minimal precipitation.
For students in the Philippines, heatwaves can have significant impacts on both their well-being and academic performance. The soaring temperatures and stifling humidity create discomfort and health risks, including heat-related illnesses such as heat exhaustion and heatstroke. These conditions can disrupt students’ ability to concentrate, leading to decreased productivity and academic achievement. Additionally, schools may lack adequate cooling systems or infrastructure to mitigate the effects of heatwaves, further exacerbating the situation for students.
Several factors contribute to the occurrence and intensification of heatwaves in the Philippines. Climate change plays a significant role, as rising global temperatures increase the frequency and severity of extreme weather events, including heatwaves. Urbanization and land-use changes also contribute, as concrete structures and asphalt roads absorb and retain heat, creating urban heat islands. Deforestation and environmental degradation can further exacerbate heatwaves by reducing the natural cooling effects of forests and green spaces.
Overall, heatwaves in the Philippines present multifaceted challenges for students, affecting their physical health, mental well-being, and academic performance. Addressing the factors contributing to heatwaves and implementing adaptive measures are essential for safeguarding students’ welfare and educational outcomes in the face of climate change.
Philippine Heatwaves in Recent Years
The Philippines has been experiencing an increase in the frequency and severity of heatwaves in recent years, attributed in part to climate change. According to data from the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA), heatwaves have become more common, with temperatures rising above historical averages for extended periods.
For example, in 2019, the Philippines experienced one of its hottest years on record, with numerous heatwave events documented throughout the country. These heatwaves often coincided with El Niño events, exacerbating the intensity and duration of high temperatures. Additionally, studies have shown a rising trend in the number of hot days and warm nights in the Philippines, indicative of a warming climate.
Furthermore, anecdotal evidence and reports from local communities and authorities highlight the detrimental impacts of heatwaves on public health, agriculture, and infrastructure. Instances of heat-related illnesses and deaths, crop failures, and power outages due to increased energy demand for cooling have been documented during severe heatwave episodes.
Overall, while specific statistical data may vary, the trend of increasing heatwave frequency and severity in the Philippines underscores the urgent need for climate resilience and adaptation measures to mitigate the adverse effects on society and the environment.
Heatwaves Impacts on Students’ Well-being
Physical Health
Extreme heat can have significant effects on the physical health of students in the Philippines, including dehydration, heat exhaustion, and heatstroke.
- Dehydration – Occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in, often due to sweating excessively in hot temperatures. This can lead to symptoms such as dry mouth, thirst, fatigue, and dizziness, impacting students’ ability to focus and perform academically.
- Heat exhaustion – Is a more severe condition resulting from prolonged exposure to high temperatures and inadequate fluid intake. Symptoms may include heavy sweating, weakness, nausea, headache, and fainting. Students experiencing heat exhaustion require immediate rest in a cool, shaded area and rehydration with water or electrolyte solutions.
- Heatstroke – Is the most severe heat-related illness and can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. It occurs when the body’s temperature regulation system fails, causing body temperature to rise to dangerous levels. Symptoms of heatstroke include a high body temperature (above 104°F or 40°C), confusion, agitation, seizures, and loss of consciousness. Without prompt medical attention, heatstroke can result in organ damage and death.
For students in the Philippines, where heatwaves are common, these heat-related illnesses pose a significant risk, especially during outdoor activities or in schools without adequate cooling systems. Prevention measures such as staying hydrated, seeking shade, and avoiding strenuous activities during peak heat hours are essential for protecting students’ physical health during extreme heat events. Additionally, schools and communities should have protocols in place to recognize and respond to signs of heat-related illnesses promptly to ensure the well-being of students.
Mental Health
- Increased stress: Coping with prolonged periods of high temperatures can lead to heightened stress levels among students, especially if they face challenges such as inadequate access to cooling facilities or disruptions to daily routines.
- Fatigue: Heatwaves can cause fatigue due to the body’s efforts to regulate temperature through sweating and an increased heart rate. The physical discomfort associated with heat can contribute to feelings of tiredness and lethargy, affecting students’ energy levels and motivation.
- Difficulty concentrating: High temperatures can impair cognitive function and make it challenging for students to focus and concentrate on academic tasks. Heat-related discomfort, such as sweating and discomfort, can distract students and hinder their ability to retain information and engage in learning activities effectively.
- Irritability and mood changes: Excessive heat can exacerbate feelings of irritability, frustration, and mood swings among students, leading to interpersonal conflicts and difficulties in social interactions.
- Sleep disturbances: Heatwaves can disrupt sleep patterns and quality, leading to insomnia or restless sleep. Poor sleep can further exacerbate mental health issues such as anxiety and depression among students.
Overall, the mental health impacts of extreme heat in the Philippines underscore the importance of implementing strategies to support students’ well-being during heatwave events, including providing access to cooling facilities, promoting stress management techniques, and fostering a supportive learning environment.
Emotional Health
- Anxiety: Children may experience increased anxiety during heatwaves, especially if they perceive the extreme temperatures as a threat to their safety or well-being.
- Frustration: Dealing with uncomfortable and oppressive heat can lead to feelings of frustration and irritability among children, particularly if they are unable to engage in outdoor activities or socialize as usual.
- Boredom: Heatwaves may restrict children’s ability to play outside or participate in recreational activities, leading to feelings of boredom and restlessness.
- Disappointment: Cancelled or postponed outdoor events and activities due to extreme heat can cause disappointment and sadness among children, especially if they were looking forward to participating in them.
- Helplessness: Children may feel helpless in the face of extreme heat, especially if they perceive it as a problem beyond their control. This sense of helplessness can contribute to feelings of stress and insecurity.
- Loneliness: Heatwaves may limit opportunities for children to interact with their peers, leading to feelings of loneliness and isolation, particularly if they are unable to socialize due to safety concerns or restrictions imposed during heatwave events.
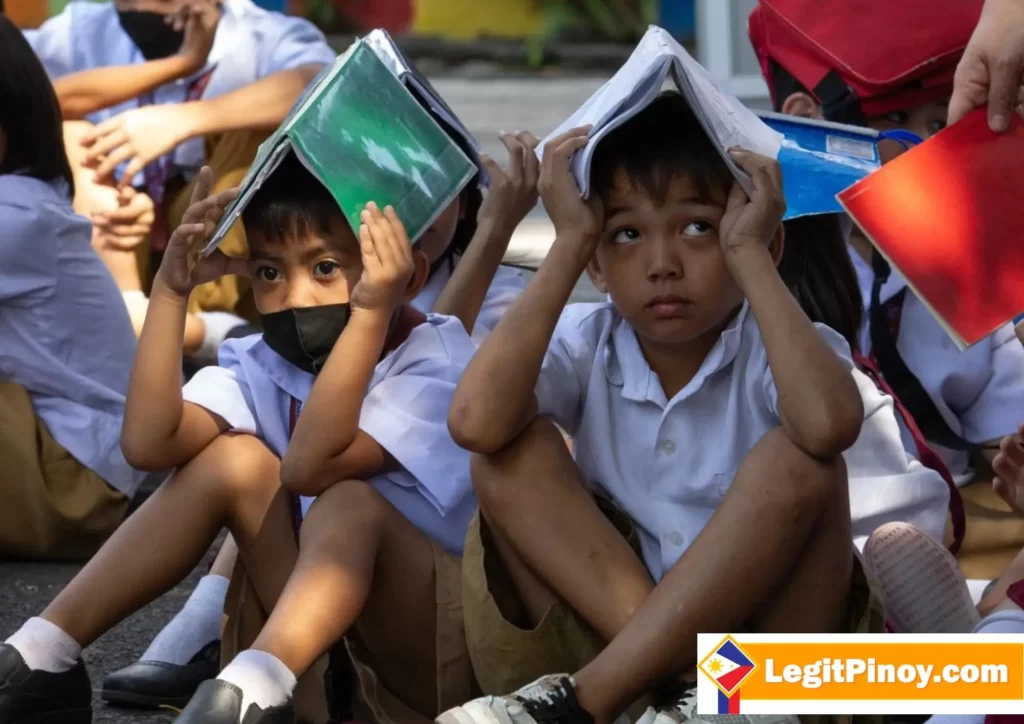

Influence of Heatwaves on Academic Performance
A. Heatwaves can significantly disrupt the learning environment in schools and universities by creating uncomfortable conditions that make it difficult for students to concentrate and engage effectively. High temperatures can lead to classrooms feeling stifling and oppressive, causing discomfort and distraction among students and teachers alike. In extreme cases, schools may even need to close or adjust schedules to ensure the safety of students and staff.
B. The effects of heatwaves on students’ ability to focus, participate actively in classes, and retain information can be profound. Heat-related discomfort can lead to increased fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating, making it challenging for students to stay engaged in lessons and discussions. Moreover, excessive heat can negatively impact cognitive function, impairing memory and critical thinking skills. As a result, students may struggle to absorb new information and perform at their best academically.
C. The possible implications of heatwaves for academic outcomes are far-reaching and can have long-term consequences for students’ educational attainment. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can lead to decreased test scores, lower performance levels, and overall academic underachievement. Heat-related stress and discomfort may also contribute to increased absenteeism and reduced motivation to learn. In addition, students from vulnerable populations, such as those living in low-income communities or without access to air conditioning, may be disproportionately affected, widening existing disparities in academic achievement. Overall, the impact of heatwaves on academic outcomes highlights the urgent need for schools and policymakers to implement measures to mitigate the effects of extreme heat on students’ learning and well-being.
Coping Strategies & Solutions
| Coping Strategies & Solutions |
| 1. Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to prevent dehydration and maintain optimal hydration levels. |
| 2. Dress appropriately: Wear lightweight, loose-fitting clothing made of breathable fabrics to stay cool and comfortable in hot weather. |
| 3. Seek shade: When outdoors, seek shade from trees, umbrellas, or buildings to avoid direct exposure to the sun’s heat. |
| 4. Use fans or air conditioning: Utilize fans or air conditioning units to cool indoor spaces and provide relief from the heat. |
| 5. Take cool showers or baths: Take frequent cool showers or baths to lower body temperature and refresh the body during hot weather. |
| 6. Plan outdoor activities wisely: Schedule outdoor activities during cooler times of the day, such as early morning or late afternoon, to minimize exposure to extreme heat. |
| 7. Limit physical exertion: Avoid strenuous physical activities during the hottest parts of the day to prevent heat-related exhaustion or heatstroke. |
| 8. Eat light and hydrating meals: Consume light and hydrating meals that are rich in water content, such as fruits and vegetables, to stay hydrated and maintain energy levels. |
| 9. Use cooling accessories: Carry portable fans, handheld misters, or cooling towels to provide instant relief from the heat when outdoors. |
| 10. Stay informed: Stay updated on weather forecasts and heatwave advisories issued by local authorities to prepare and take necessary precautions during extreme heat events. |
Key Points to consider for government action to address climate change
- Mitigation measures: Governments should implement policies and initiatives to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change. This includes transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and promoting sustainable transportation options.
- Adaptation strategies: Governments need to develop and implement adaptation strategies to help communities cope with the impacts of climate change, including heatwaves. This may involve improving infrastructure resilience, enhancing early warning systems, and implementing heatwave response plans to protect vulnerable populations.
- Public awareness and education: Governments should prioritize public awareness and education campaigns to inform citizens about the risks associated with heatwaves and climate change. This can help empower individuals to take proactive measures to reduce their carbon footprint, adapt to changing climate conditions, and protect their health and well-being.
- International cooperation: Climate change is a global issue that requires coordinated action at the international level. Governments should collaborate with other countries to negotiate and implement agreements aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions, promoting sustainable development, and building resilience to climate impacts.
- Investment in research and innovation: Governments should invest in research and innovation to develop new technologies, strategies, and solutions for addressing climate change and reducing the frequency and severity of heatwaves. This includes funding scientific research, supporting climate-related initiatives, and fostering innovation in renewable energy, agriculture, and urban planning.
By advocating for government action on climate change, individuals and organizations can help drive positive change and contribute to building a more sustainable and resilient future for all.
Conclusion
Throughout this article, we have explored the profound impact of heatwaves on students in the Philippines. We have highlighted how extreme heat can lead to physical health issues such as dehydration, heat exhaustion, and heatstroke, as well as emotional and mental health challenges including increased stress, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating. These effects can significantly disrupt students’ well-being and academic performance, underscoring the urgent need for proactive measures to mitigate the impact of heatwaves on this vulnerable population.
As we conclude, it is imperative for individuals, institutions, and policymakers to prioritize the health and safety of students amidst the growing threat of heatwaves and climate change. We must take proactive steps to provide adequate cooling facilities in schools, implement heatwave response plans, and educate students about the importance of staying hydrated and seeking shade during hot weather. Additionally, we call on policymakers to prioritize climate action, invest in renewable energy and sustainable infrastructure, and develop comprehensive strategies to adapt to the changing climate. By working together, we can create a safer and healthier environment for students in the Philippines and around the world.
You May Also Like
We Also Recommend
- Otso CC
- Philboss
- Swerte99
- Peraplay
- Lodi646
- Jiliplay Casino
- 7bet
- OKbet
- Philwin
- BK8
- Betso88
- Phspin
- YY777
- Lovejili
- Peso63
- WJslot Casino
- SSbet77
- 1xbet
- MNL77
- Lodigame Casino
- JiliCC casino
- Money88
- W500
- Winph
Advertisement


Jill Lynn is a versatile blogger and content creator who loves writing about a variety of topics. From travel and lifestyle to food and wellness, she shares her experiences and insights with readers around the world. With her authentic voice and engaging storytelling, Jill has built a strong online presence and a supportive community of followers. Her passion for writing and dedication to producing quality content continue to inspire others on their own journeys.
